Concrete, often hailed for its durability, isn’t immune to the hidden threat of corrosion. When steel reinforcement within concrete structures corrodes, it compromises the integrity, leading to safety risks and costly repairs. But how can you assess corrosion without causing further damage to the structure? That’s where non-destructive testing (NDT) methods come into play, offering innovative solutions for corrosion assessment.
Explore 12 Futuristic Technology Trends Solving Concrete's Biggest Challenges.
Why Corrosion in Concrete Matters

Concrete structures rely on embedded steel reinforcement to maintain strength. However, factors like chloride ingress and carbonation can trigger corrosion in the steel, leading to cracks, spalling, and eventual failure if not addressed promptly. Traditional methods of testing corrosion often involve destructive techniques that risk damaging the concrete itself. In contrast, non-destructive concrete testing offers a proactive, efficient, and safe approach to diagnosing corrosion before it escalates into a structural problem.
The Shift from Destructive to Non-Destructive Concrete Testing
In the past, destructive testing methods, such as core sampling or cutting out sections of concrete, were commonly used to assess corrosion. While these methods can provide detailed information, they are invasive, time-consuming, and expensive. More importantly, they often leave the structure compromised in the process. As the construction industry evolves, there’s a growing demand for more sustainable and cost-effective approaches. This leads to the rise of non-destructive testing methods for corrosion assessment.
NDT offers a solution that balances precision with preservation. These advanced techniques enable the evaluation of concrete’s condition without affecting its structural integrity.
Read more about these methods here.
Top NDT Methods for Corrosion Assessment
Several NDT methods stand out when it comes to evaluating corrosion in concrete structures. These methods provide detailed insights into the state of the embedded reinforcement without causing any damage. Here are the most widely used techniques:
1. Electrochemical Measurements
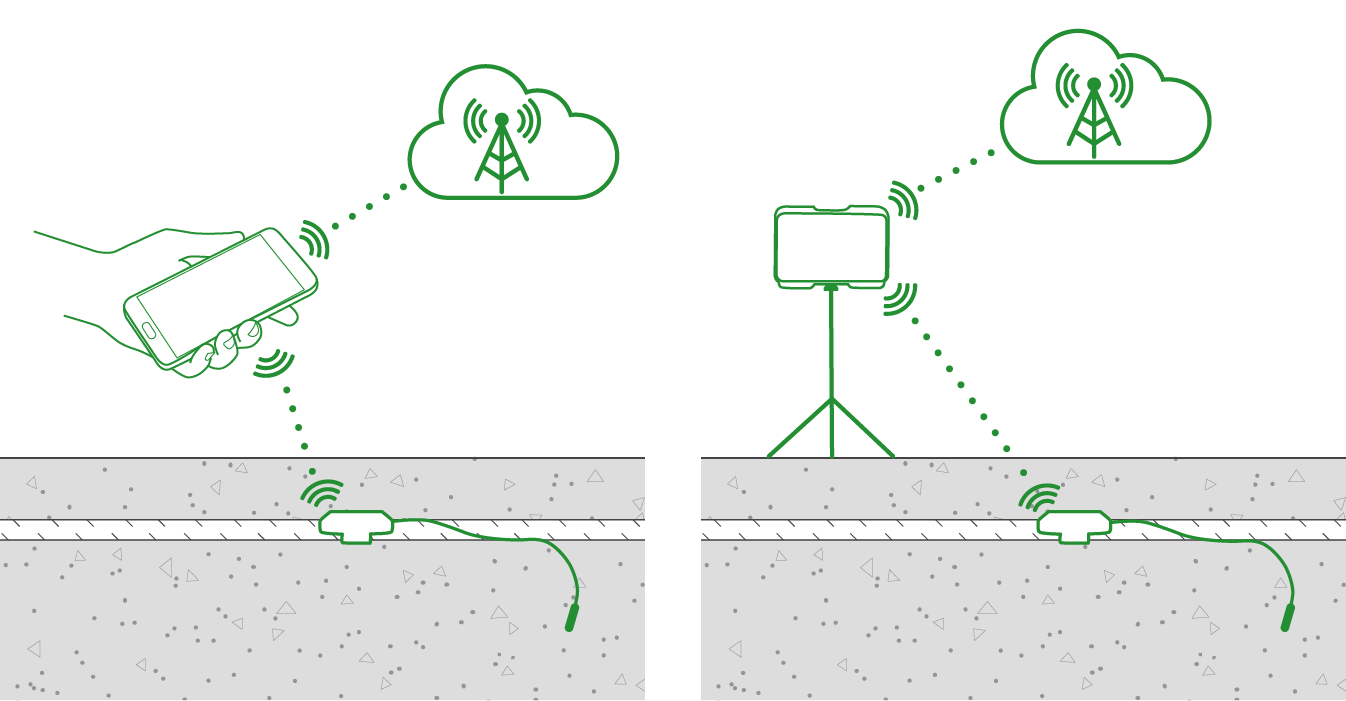
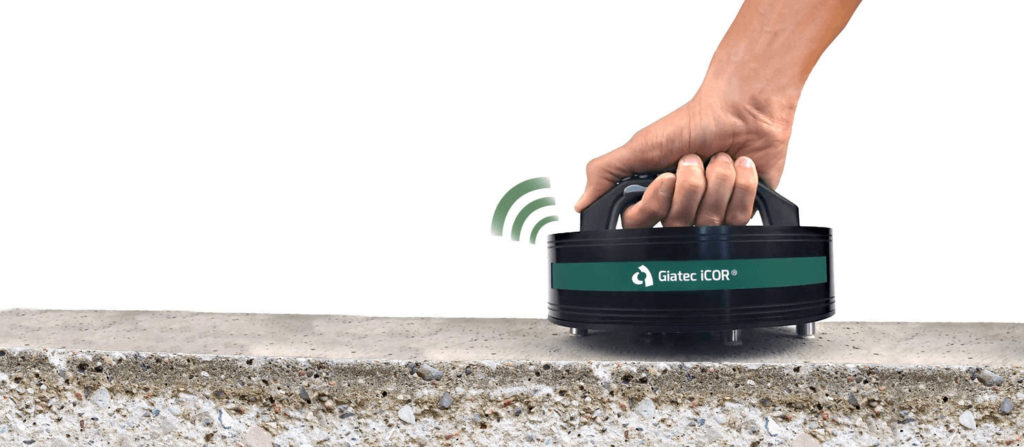
Electrochemical methods are commonly used to measure the corrosion rate of the steel embedded in concrete. One of the most efficient tools in this category is Giatec’s iCOR®, which employs patented CEPRA technology to provide wireless, non-invasive corrosion rate measurements. Unlike traditional methods, iCOR® offers real-time data with minimal surface preparation, making it a powerful solution for engineers looking to monitor corrosion over time.
2. Half-Cell Potential Mapping
Half-cell potential testing involves placing a reference electrode on the concrete surface and measuring the potential difference between the electrode and the embedded steel. This method can indicate areas where corrosion is likely to occur, though it doesn’t measure the corrosion rate directly. However, it’s a useful tool for identifying at-risk zones in large structures.
3. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
GPR is another popular NDT method that can detect anomalies in concrete structures, such as voids, cracks, and delaminations that may be caused by corrosion. It works by sending radar waves into the concrete and interpreting the reflected signals. GPR provides an excellent overview of the internal state of the concrete and can help in identifying areas that may need further testing.
4. Infrared Thermography
This method uses infrared cameras to detect temperature variations on the concrete surface, which may indicate underlying issues such as moisture ingress or corrosion. Infrared thermography is a useful tool for initial inspections, offering a quick and visual way to assess large areas.
Giatec’s iCOR®: Revolutionizing Corrosion Detection
At the forefront of NDT innovation is Giatec’s iCOR device, which has revolutionized how we assess corrosion in concrete. Its wireless, easy-to-use system allows for rapid corrosion assessment without damaging the structure. By combining multiple testing techniques, including electrical resistivity and polarization resistance, iCOR provides a comprehensive picture of the concrete’s health. Plus, with its user-friendly interface and real-time data capabilities, it empowers engineers to make informed decisions quickly.
Using the iCOR enables a higher degree of accuracy while significantly reducing the time and costs associated with traditional corrosion assessment methods. It’s a game-changer for those working on large infrastructure projects where regular corrosion monitoring is essential.
The Future of Corrosion Monitoring

As the demand for sustainable infrastructure grows, the need for innovative, non-destructive corrosion monitoring tools becomes even more crucial. The future lies in integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning into NDT systems, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing the risks associated with corrosion-related failures.
At Giatec, we are committed to leading this charge with solutions like iCOR and our SmartRock® sensors, ensuring that concrete structures remain safe, durable, and efficient for years to come.