Construction remains one of the most hazardous industries in the world. In the U.S. alone, the annual cost of work-related injuries and illnesses exceeds $97 billion. These costs include far more than medical treatment; they extend to lost productivity, project delays, insurance claims, legal exposure, and long-term damage to company reputation.
SmartRock® Long Range Savings for Big Projects
Yet studies show that for every dollar invested in safety, organizations save between $4 and $6. That return rivals or surpasses many capital investments. It’s no longer enough to treat safety as a compliance checkbox. It’s a value multiplier, shaping a company’s ability to win contracts, retain workers, and deliver projects on time and under budget.
Firms that prioritize safety stand out in an industry that increasingly favors reliability, transparency, and responsible leadership. The industry is evolving, so must the mindset toward safety. In this blog, we’ll look at the evolving role of safety in construction, how new technologies, standards, and leadership approaches are transforming it from a cost center into a competitive edge.
Setting the Tone: Leadership Drives Safety Culture
Safety begins long before workers step onto a jobsite. It starts with leadership.
When executives and managers visibly commit to safety, it sends a clear message: safety is non-negotiable. Leaders who model safe behavior set the tone for the entire jobsite. Showing up with the right gear, joining safety meetings, or supporting training initiatives signals that safety matters. Even small actions like wearing PPE during site visits or starting meetings with a safety reminder demonstrate accountability and consistency.

When managers follow the same standards they expect from workers, they build trust and credibility. Workers take notice when managers don’t cut corners. when they see investments being made in protective equipment, hazard controls, and time for proper onboarding, they understand that safety is more than policy; it’s part of how the job gets done.
Transformational and visible leadership styles are among the most effective approaches to improving safety. Active, engaged leaders improve morale, encourage open communication, and promote employee participation in safety efforts, embedding safety deeply into daily routines.
An empowered safety culture also requires shared responsibility. Every team member should feel accountable not just for their own safety, but for their coworkers’ as well. It encourages open reporting, hazard identification, and problem-solving without blame. Over time, this culture pays off through reduced incidents, stronger team cohesion, and better project performance.
Want to learn how to foster a true culture of safety on your jobsite? Read more about construction management here!
The Fatal Four Hazards: Construction’s Leading Risk
Every construction site faces a myriad of hazards, but a few types are responsible for the majority of severe injuries and fatalities. OSHA has identified the “Fatal Four” hazards: falls, struck-by incidents, caught-in/between accidents, and electrocutions – as the top killers on construction sites, accounting for roughly 60% of construction worker deaths annually. Managing these key risks is both a moral obligation and a business necessity. Let’s break them down:
- Falls
Falls from height remain the leading cause of construction fatalities, responsible for nearly 40% of construction deaths each year, according to the Infrastructure Health and Safety Association (IHSA). Whether it’s a fall from a roof, scaffolding, or ladders, the outcomes are often devastating. Preventing these starts with planning, then providing equipment, and training workers, the classic “Plan. Provide. Train.” formula championed by OSHA.
Best practices include:
- Using fall protection gear like harnesses, lanyards when working over 6 feet.
- Installing guardrails, safety nets, and covers for openings.
- Conducting regular scaffold and ladder inspections.
- Training crews to spot hazards and use protection properly.
Following this formula makes falls largely preventable, even in high-risk environments.
- Struck-by Incidents
These involve workers being hit by moving vehicles, flying debris, or falling objects. Struck-by events contributed to roughly 17% of construction deaths in 2023.
Mitigation strategies:
- Establish separate routes for vehicles and pedestrians, as well as use internal traffic control plans (ITCPs).
- Require high-visibility vests and helmets.
- Use spotters, proximity sensors, and backup cameras.
- Secure tools and materials at height to prevent drops.
- Caught-in/Between Accidents
This category includes trench collapses, equipment entrapments, and incidents involving rotating or moving parts. While a smaller percentage (~6%) of fatalities, they are often gruesome.
Strong defenses include:
- Shoring, sloping, or using trench boxes for excavations deeper than five feet
- Enforcing strict lockout/tagout procedures during maintenance.
- Installing guards on machinery.
- Training crews to avoid compressed spaces and moving parts.
- Electrocutions
While less often cited than falls, electrocutions remain dangerous; construction workers are about four times more likely to be electrocuted than those in other industries. In 2022, electrocution accounted for nearly 6% of fatal injuries (as part of broader contact exposures). Electrical injuries can be fatal even without falls, and they often also lead to falls when working at heights.
Effective prevention includes:
- Identifying and marking overhead lines and maintaining safe distances or de-energizing when possible.
- Using Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) on all temporary wiring.
- Restricting electrical work to qualified personnel and following lockout/tagout rules.
- Using insulated tools and PPE like rubber gloves.
- Planning electrical safety into site layout, using cordless or low-voltage systems where feasible.
While these four hazards account for the majority of construction fatalities, they are also largely preventable with the right combination of planning, protective equipment, training, and continuous monitoring. Understanding these hazards is only the first step; equipping teams with proper protective gear, enforcing safety protocols, and leveraging technology to monitor risks are what truly make worksites safer.
The Foundation of Every Site: Equipment and PPE Done Right
Safety begins with basic gear. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a worker’s first defense against injury and remains critical even in the most high-tech environments.
Importantly, PPE and vigilance provide a last line of defense against all these hazards. Every worker should at a minimum have a hard hat, safety boots, high-visibility clothing, and safety glasses on site. Depending on the task, additional PPE like hearing protection, gloves, face shields, or respiratory protection might be needed.
What’s changing is how this equipment is tracked and verified. Digital checklists and wearable devices now help supervisors confirm that workers are outfitted properly before entering hazardous zones. For instance, smart helmets and vests can alert wearers to loud environments or excessive exposure times, reducing risks from fatigue or overexertion.
Advancements include AI-driven PPE compliance systems that continuously monitor PPE usage via cameras and sensor integrations, enabling real-time alerts when workers are missing required protection. This automation closes gaps left by manual inspections and dramatically reduces risk.
Connected Construction: Real-Time Safety Insights
A decade ago, most construction sites relied on paper logs, word-of-mouth alerts, and reactive safety management. Today, the rise of connected technology has introduced real-time visibility, allowing project teams to detect and respond to risks as they emerge.
Wearables: Monitoring at the Source
This technology monitors worker motion, posture, heart rate, and location. If someone is motionless for too long or enters a restricted zone, alerts are automatically triggered. Devices like Spacebands alert workers when they enter a dangerous zone or forget crucial PPE, like hearing protection, and log these near-misses to dashboards for analysis. This real-time visibility helps safety managers intervene before incidents occur.
Environmental and Equipment Sensors: The Wider Picture
Connected sensors inside buildings can detect air quality hazards (dust, VOCs, gas), noise spikes, or weather threats (e.g., sudden high winds near cranes). Alerts are sent instantly to supervisors’ devices so work can be paused and protections deployed. Even equipment contributes; AI-enabled cranes and trucks now detect obstacles or workers and can auto-brake to prevent collisions.
Smart Concrete Monitoring: Built-In Protection
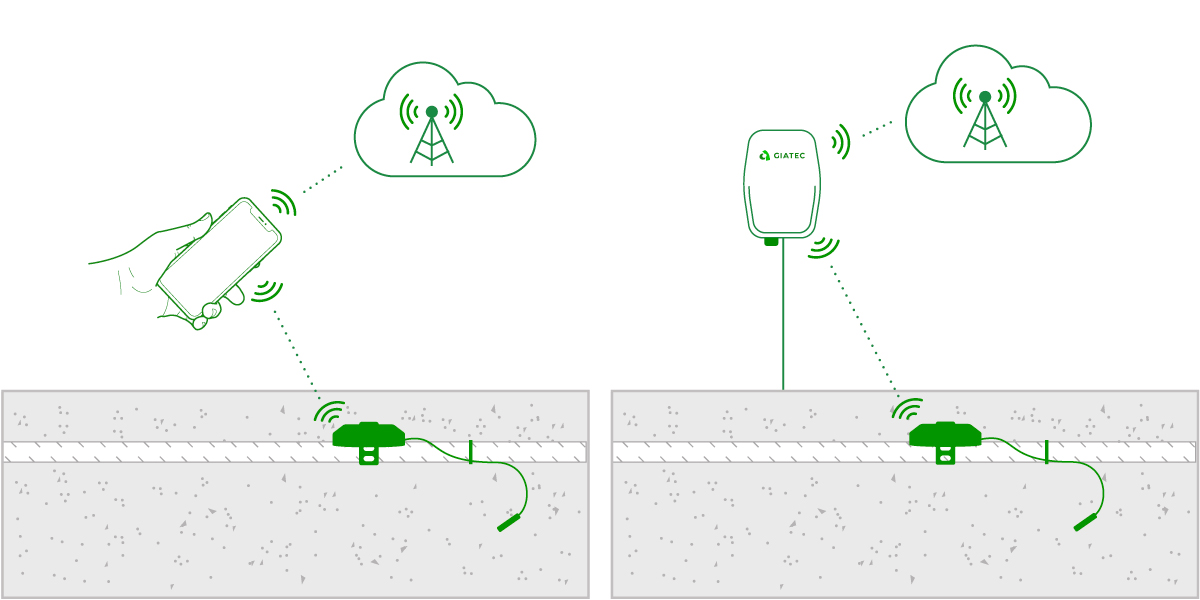
Traditional methods for assessing concrete strength are often based on guesswork or postponed testing. Traditional concrete monitoring often involved wired thermocouples that had to be installed, connected, and manually read. These systems were prone to cable damage, required workers to enter potentially unsafe areas for readings, and added clutter that created trip hazards. Such limitations not only slowed workflows but also introduced additional safety risks on site.
Now, with wireless concrete sensor like SmartRock®, you get continuous temperature and strength updates, right from the rebar to your mobile device. This visibility removes guesswork, helping teams avoid dangerous premature loading and stay ahead of the schedule. Sensors sync seamlessly with the Giatec 360™ dashboard to deliver real-time alerts, even on large sites.
These tools now often integrate with AI-powered safety management modules that analyze sensor inputs, video feeds, and environmental data to predict unsafe behaviors or hazard buildup before incidents occur.
Flood Testing Laboratories Inc. (FTL), a well-established construction material testing company in Chicago, faced exactly these challenges with their wired maturity systems: expensive, specialized readers, vulnerable wires, and complicated data sharing among team members. Seeking a modern solution, FTL adopted SmartRock wireless sensors for real-time concrete maturity monitoring.
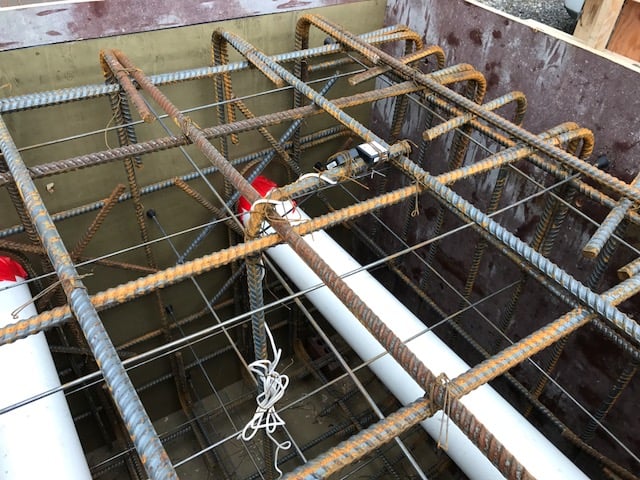

With SmartRock, temperature and strength data are continuously transmitted from the rebar directly to mobile devices via Giatec’s app, eliminating the need for costly readers and minimizing hazards from wires. Sensors attach easily to the formwork, and once concrete is poured, they calculate maturity and strength following ASTM C1074 standards. The result is safer, more accurate monitoring that can be accessed from anywhere on the jobsite.
FTL reports significant benefits from SmartRock: improved project efficiency, optimized scheduling for curing, formwork removal, and post-tensioning, and fewer accidents as sensors remain embedded and out of harm’s way. The system also simplifies data access, no specialized equipment is needed, and information can be shared instantly with contractors, giving teams a competitive edge in bidding and project delivery.
Interested in learning how SmartRock transformed FTL’s workflows? Read the full case study here!
From Paper Plans to Smart Safety Management
Planning remains a cornerstone of effective safety. But the way teams develop, track, and enforce safety plans has changed dramatically. Outdated manual practices (like wired monitors or paper checklists) are rapidly being replaced by connected, automated systems.
Digital tools now make it simple to:
- Develop custom safety plans for each project, tailored to site-specific risks
- Automated tracking of training, certifications, and site access
- Conduct mobile audits and inspections, complete with photo evidence and timestamped reports
- Receive instant alerts when high-risk activities begin without proper controls
The shift to fully automated compliance documentation and real-time certification tracking eases administrative work, boosts audit readiness, and keeps projects aligned with stricter regulatory standards, enhancing both safety performance and operational transparency. By replacing outdated methods like wired monitors or paper checklists with connected, automated systems, sites become not only more efficient but fundamentally safer. Fewer human errors, faster responses to issues, and seamless integration of safety into daily tasks are now achievable across every project.
Looking to strengthen your safety and project management practices? Learn how in our blog here!
SmartRock® Long Range Savings for Big Projects
Psychosocial Hazards and the Future of Construction Site Safety
Construction safety has traditionally focused on physical risks. However, an emerging concern is the mental and emotional well-being of workers. Long hours, high physical stress, deadline pressure, and separation from family can affect mental health, and mental health affects safety
Fatigue, anxiety, and distraction all raise the risk of errors and incidents. That’s why forward-thinking firms now incorporate psychological safety into their overall approach.
This includes:
- Training Supervisors: Equipping leaders with skills to offer support and recognize signs of distress.
- Raising Awareness: Launching mental health awareness campaigns and encouraging workers to speak up about stress or exhaustion.
- Providing Support: Offering Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) that include counseling services, and assigning “mental health first aid” volunteers on-site.
- Improving Work Organization: Limiting excessive overtime, ensuring regular rest days, and adjusting schedules to avoid unreasonable pressure.
As the industry evolves, attention is shifting from solely addressing physical hazards to also focusing on the human element. A safe workplace now means holistically safe, protecting workers from harm both seen and unseen. Companies that prioritize mental health and supportive culture tend to have superior safety records and project outcomes. Investing in worker well-being is not just the right thing to do; it’s also smart business.
Studies confirm that psychologically safe environments foster open hazard reporting, encourage safety idea sharing, and mitigate the culture of blame, significantly reducing accident risks. Construction has one of the highest rates of suicide among all industries. Ignoring psychosocial risk undermines even the best physical protections. Addressing it builds stronger teams and more resilient projects.
Greener, Safer Sites: Sustainability as a Safety Strategy
There’s growing overlap between sustainability and safety. Practices that reduce environmental impact often improve working conditions and construction site safety.
Here are some key practices and tools:
| Section | Key Points | Examples / Tools |
| Sustainability and Safety | Green practices enhance safety; sustainable workplaces protect workers, environment, and long-term business. | Integrated safety and sustainability programs |
| Hazard Prevention & Pollution Control | Reduces risks to workers and environment; toxic material management prevents exposure and accidents. | Low-VOC paints, non-toxic materials, spill containment |
| Designing for Safety | Sustainable building design improves visibility, reduces respiratory hazards, and lowers fire risk. | Natural lighting, ventilation, fire-resistant materials, waste management |
| Workforce Health & Ergonomics | Ergonomics and wellness reduce injuries and fatigue; healthy workers are safer and more productive. | Prefabricated components, powered lifting, hydration, stretch breaks |
| Culture, Compliance & Innovation | Leadership and values-driven culture reinforce safety; technology reduces exposure and environmental impact. | Integrated EHS systems, drones, concrete maturity sensors, Giatec SmartMix AI |
| Conclusion | Greener sites are safer; integrating sustainability and safety lowers incidents, ensures compliance, and future-proofs projects. | Safety-first culture, streamlined training, reduced environmental impact |
Greener construction sites are safer construction sites. By reducing toxic chemicals, cutting waste, improving work methods, and prioritizing employee wellness, firms create safer, more efficient worksites. Treating construction site safety and sustainability as complementary priorities lowers incident rates, ensures compliance, strengthens brand reputation, and future-proofs projects.
Want to integrate sustainability into every project? Download our guide here!
Staying Ahead: New Standards and the Digital Compliance Shift
Construction safety has always been guided by regulations and standards, from OSHA requirements to local building codes, but the safety mandate in the modern era is evolving. Compliance remains the foundation, yet forward-thinking companies are moving beyond mere compliance toward a more proactive, technology-enabled approach to safety. Executives should understand both the letter of the law and the emerging best practices that are quickly becoming industry standard.
Custom Safety Plans and Training
One-size-fits-all manuals are no longer enough. Site-Specific Safety Plans (SSSPs) and digital templates allow teams to tailor hazard assessments and control measures to each project. Digital templates allow safety managers to quickly build plans, incorporate project-specific details like crane usage or trench depths, and keep them updated in real time. Tracking training and certifications has also gone digital, with QR-coded badges and software platforms ensuring every worker is qualified for high-risk tasks.
Proactive Monitoring
Technology is transforming compliance. SmartRock Pro tracks concrete curing and environmental conditions in real time, eliminating risks from manual readings. Utilizing Giatec’s patent-pending Concrete Electro-Mechanical Microstructural Analysis (CEMMA) technology, SmartRock Pro offers self-calibrating, mix-independent strength monitoring. This advancement ensures accurate, real-time insights without the need for manual calibration, adapting to varying concrete mixes and environmental conditions.
Beyond concrete, wireless solutions improve electrical safety and equipment monitoring. Battery-powered tools, wireless lighting, and telematics for machinery may also reduce trip hazards, electrocution risk, and equipment failures. Integrating these tools into a digital safety system allows teams to detect potential risks early and respond before incidents occur.
Standards and Certifications
Voluntary standards like ISO 45001 push companies beyond minimum requirements, encouraging continuous improvement and worker participation. Clients increasingly evaluate contractors based on metrics such as Experience Modification Rate (EMR) and Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR), making proactive safety a competitive advantage.
Regulators are also updating requirements to keep pace with technology. For instance, OSHA’s adoption of Safety Management Systems (SMS) has led to a 20% reduction in workplace injuries among companies that have implemented them. These systems integrate processes like hazard identification, risk assessment, and incident reporting, often utilizing digital tools such as wearable sensors and AI-powered monitoring to enhance compliance and safety outcomes.
Conclusion
Safety has long been a requirement in construction but in 2025, it’s also a business advantage. Strong leadership, a proactive safety culture, and technology-driven solutions now work together to protect workers, improve productivity, and enhance project outcomes.
Executives play a critical role in setting the tone: investing in smart safety, supporting rigorous training, and fostering a culture where every worker feels accountable. Integrating safety with operational planning, sustainable practices, and worker wellness creates multiple benefits: safer sites, stronger reputations, and more profitable projects. As sites become more connected, efficient, and accountable, one thing is clear: The smartest jobsites are the safest. And in today’s industry, that’s what defines success.
Learn more about how to mitigate risks and improve project safety with maturity monitoring. Download our Temperature Monitoring Whitepaper today!